Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Approximate floating-point multiplication¶
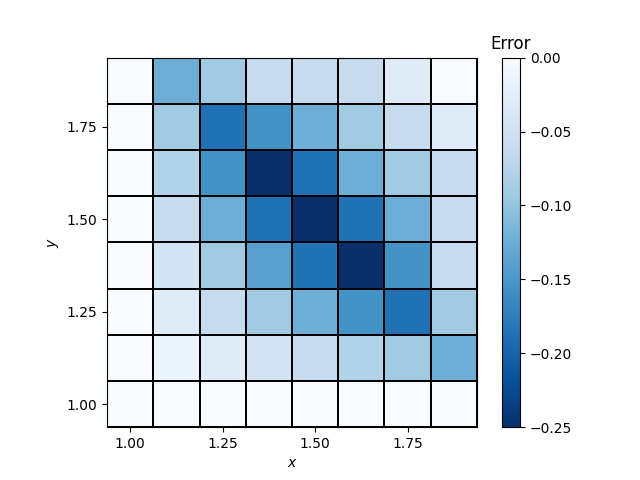
This example compares an approximate floating-point multiplication to the mathematically correct result. The approximation is based on Mitchell’s logarithm approximation and the reference is the unquantized result.
(Example inspired from T. Lindberg and O. Gustafsson, “Exact Eight-Bit Floating-Point Multiplication Using Integer Arithmetic”, in Proc. Asilomar Conf. Signals Syst. Comput., 2025.)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import ticker
import apytypes as apy
EXP_BITS, MAN_BITS = (4, 3)
input_values = apy.fullrange(1, 2, exp_bits=EXP_BITS, man_bits=MAN_BITS)
xx, yy = apy.meshgrid(input_values, input_values)
# Calculate the reference using a format wide enough to capture the exact result
ref = xx.cast(EXP_BITS, 2 * MAN_BITS) * yy
def approx_mul(x, y):
return apy.APyFloat.from_bits(
x.to_bits() + y.to_bits() - (x.bias << x.man_bits), EXP_BITS, MAN_BITS
)
result = apy.zeros_like(ref, exp_bits=EXP_BITS, man_bits=MAN_BITS)
for xi, x in enumerate(input_values):
for yi, y in enumerate(input_values):
result[xi, yi] = approx_mul(x, y)
error = result - ref
Plot the results
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set_xlabel(r"$x$")
ax.set_ylabel(r"$y$")
ax.set_aspect("equal")
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(2 * 2**-MAN_BITS))
ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(2 * 2**-MAN_BITS))
pcol = ax.pcolormesh(xx, yy, error, ec="k", lw=0.1, cmap="Blues_r")
cbar = fig.colorbar(pcol)
cbar.ax.set_title("Error")
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.100 seconds)